Hair loss in women has multiple causes and requires different treatment approaches depending on the underlying issue. In many cases, women lose hair due to hormonal changes, genetics, health issues, stress, or problems with hair growth.
Treatment options include medical therapies that slow hair loss and support regrowth. There are also procedural solutions for cases where follicles no longer respond to medication, similar to approaches discussed in female hair transplant success rate evaluations.
Understanding the cause is essential, since effective treatment depends on whether the hair loss is temporary, progressive, or linked to an underlying condition.
Key Takeaways
- Hair loss in women usually has more than one cause, and understanding what is the reason for hair fall in females requires evaluating hormones, genetics, stress, and underlying medical conditions.
- Early signs such as crown thinning or widening of the part often resemble patterns seen in hair transplant on black female cases of diffuse thinning.
- Accurate diagnosis, including medical history and basic lab tests, is essential to decide whether hair loss is temporary, progressive, or linked to a treatable condition.
- The most effective way to treat hair loss depends on the cause and may include medical therapy, nutritional correction, or procedural options when follicles no longer respond to medication.
What Causes Hair Loss in Women
Hair loss in women rarely has a single cause. When patients ask what causes hair loss in women, clinicians usually evaluate multiple contributing factors at once.
Hormonal changes, genetics, and systemic health issues often interact and affect the hair growth cycle. Understanding these causes helps determine whether hair loss is temporary or progressive.
Common causes of hair loss in women include:
- Hormonal changes related to pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid imbalance
- Genetic predisposition and family history
- Nutritional deficiencies such as iron or vitamin D
- Chronic illness or autoimmune disease
Why am I losing so much hair female
Many women experience sudden increases in hair shedding after stress, illness, or significant life changes. This pattern can be alarming, especially when large amounts of hair are seen during washing or brushing.
In most cases, the follicles remain intact, but the hair shifts prematurely out of the growth phase. This leads to noticeable shedding rather than permanent hair loss.
Which hormone causes hair loss in females
Hormones play a central role in hair regulation. Estrogen supports hair growth, while androgens can shorten the growth cycle in susceptible follicles.
When estrogen levels drop, such as during menopause, hair may become thinner and grow more slowly. Hormonal sensitivity is a key factor in female pattern hair loss.
Genetics and medical conditions
A strong family history increases the likelihood of long-term thinning. Certain medical conditions, including thyroid disorders and anemia, are also common contributors.
In these cases, hair loss includes diffuse thinning rather than a single bald patch. Treating the underlying condition often improves hair density.
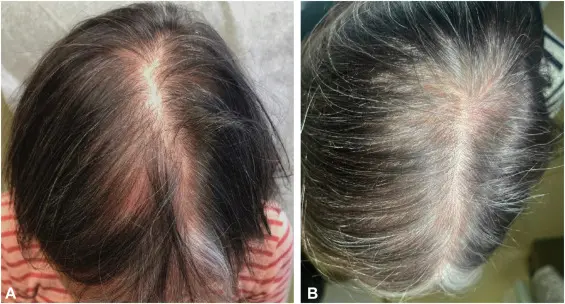
Hair Thinning in Women: Early Signs
Hair thinning women often notice changes before visible bald spots appear. Early signs are subtle and may develop over months or years. Recognizing these signs allows earlier evaluation and treatment planning.
Widening part and volume loss
A widening part is one of the earliest indicators of thinning. Hair may feel less dense, especially at the crown. This pattern does not usually involve a receding hairline.
Increased hair shedding
Shedding beyond the normal daily range can indicate disruption in the hair cycle. Women may notice more hair on pillows or clothing and begin to worry they will lose hair permanently. Persistent shedding should prompt medical review.
Hair Loss in Women Over 40

Hair loss in women over 40 often reflects cumulative hormonal and genetic influences. Aging alone does not cause hair loss, but it alters how follicles respond to hormonal changes. Menopause is a frequent turning point for many patients.
Hormonal changes and menopause
During menopause, declining estrogen shortens the growth phase and slows regrowth. Hair becomes finer and less resilient over time. Thinning is more common than complete bald spots in this age group.
What Does Hair Loss From Stress Look Like
Stress-related hair loss typically presents differently from genetic thinning. It often appears suddenly and affects the entire scalp rather than one area.
Sudden shedding and telogen effluvium
Telogen effluvium occurs when physical or emotional stress pushes many hairs into the resting phase at once.
This condition differs from chronic thinning that may eventually require when you should get hair transplant evaluation..
Signs of stress-related hair loss include:
- Diffuse shedding across the scalp
- Increased hair loss during washing or brushing
- No permanent bald spots or scarring
Common Types of Hair Loss in Women
Understanding the types of hair loss helps explain why treatments vary. Each type has a distinct cause and progression.
Female pattern hair loss
Female pattern hair loss causes gradual thinning along the part and crown. It progresses slowly and rarely causes frontal recession. Genetic sensitivity to hormones is the primary driver.
Diffuse and patchy hair loss
Diffuse hair loss spreads evenly across the scalp, while patchy loss creates visible bald spots. Patchy loss may indicate autoimmune conditions. Accurate diagnosis prevents inappropriate treatment.
How Hair Loss Is Diagnosed
Diagnosis is a critical step before treatment. A structured medical evaluation improves safety and treatment outcomes.
Medical history and scalp evaluation
Physicians review medications, stressors, and family history. Scalp examination assesses follicle health, density, and signs of inflammation. This helps determine whether hair loss is temporary or progressive.
Blood tests and hormone checks
Blood testing may include iron levels, thyroid function, and hormone panels. Many cases of hair fall for ladies improve once deficiencies are corrected. Diagnosis guides targeted treatment rather than trial-and-error approaches.
Hair Loss Treatment for Women
Hair loss treatment for women focuses first on slowing or stopping further loss. Treatment plans depend on diagnosis and patient goals.
How to stop hair fall immediately
Immediate management may include correcting deficiencies or adjusting medications. Medical therapy can reduce excessive shedding, though results are not instant. Patients should understand potential side effects before starting treatment.
Medical and prescription treatments
Common options include topical and oral therapies that support the growth phase. These treatment options require consistent use to maintain results. They aim to stabilize follicles rather than create new ones.
How to Regrow Thinning Hair Female
@trichogenics Hair transplants in women are a little bit more complicated. We always want to aggressively treat pattern hairloss before attempting surgery. Always exhaust medical therapy first before jumping into an irreversible surgery. #hairtransplant #femalehairtransplant #femalehairloss #hairtransplantturkey #minoxidil #finasteride #spirinolactone
♬ original sound - Trichogenics
Regrowth depends on whether follicles remain viable. Some women respond well to medical care, while others require procedural intervention.
Natural remedies and vitamins
Vitamins support hair health when deficiencies exist but do not reverse genetic loss. Iron, vitamin D, and zinc are commonly assessed. Supplements should follow medical guidance.
Clinical and surgical options
When follicles no longer respond to medication, hair transplants may be considered. Modern techniques include FUE and DHI with Choi pen implantation, performed in licensed medical clinics.
These procedures require certified physicians, sterile operating rooms, and structured follow-up care.
Examples of clinical settings and pricing:
- Greece – USD 3,500–6,000 for physician-performed FUE, including graft extraction, implantation, anesthesia, and follow-up
- Israel – USD 4,000–6,500 for doctor-led FUE or DHI, depending on graft count
- Turkey – USD 1,800–2,800 in high-volume clinics, often with technician-led procedures and limited medical supervision
Price differences reflect who performs the procedure, time per patient, and level of oversight. Physician-led care reduces risks such as overharvesting and unnatural density.
When to See a Hair Specialist
Women should seek specialist care when hair loss persists, worsens, or affects daily life.
Early evaluation improves treatment planning and reduces unnecessary procedures. A medical consultation clarifies expectations and safety considerations. Timely care supports better long-term outcomes.
Why Choose Trichogenics?
All procedures are performed only by doctors
The uniqueness of Trichogenics lies in its strict medical process; only certified doctors perform every transplant. No technicians or unqualified assistants are involved. Choosing a clinic with proven experience in hair transplants can make all the difference.
Meet Dr. Asi and Dr. Eric Peretz

The two doctors leading Trichogenics, Dr. Asi Peretz and Dr. Eric Peretz, are recognized leaders in the field. Their extensive experience, attention to detail, and focus on natural results make Trichogenics the best choice.
Contact Trichogenics today to schedule a personal consultation and get a clear, doctor-led plan for your hair restoration.



