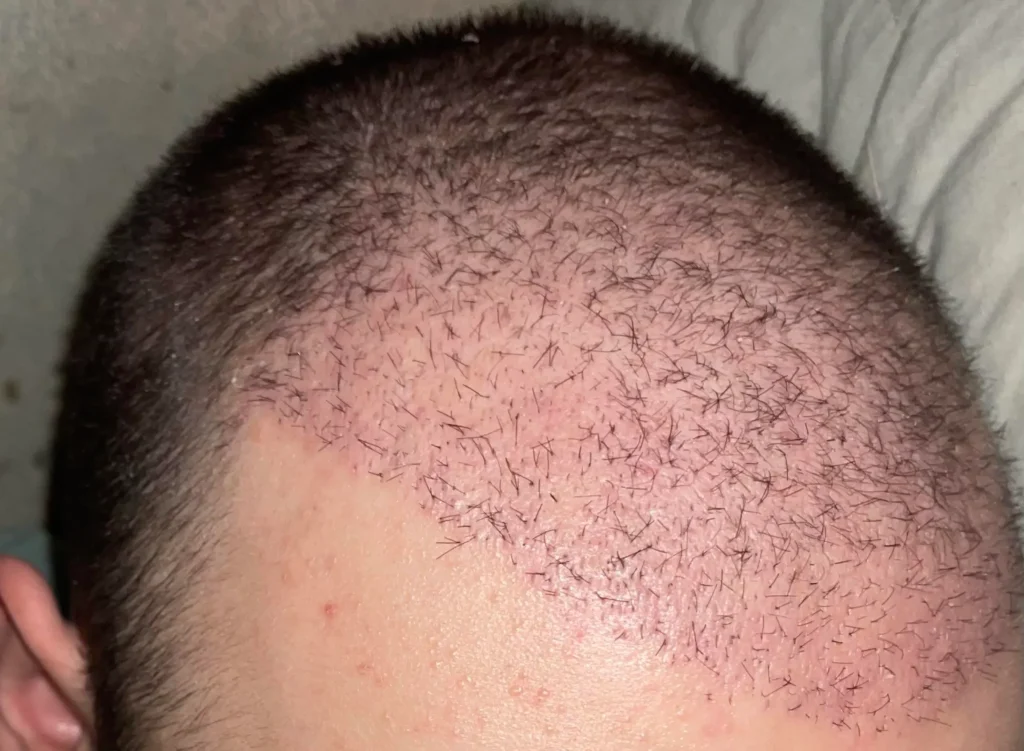
The hair transplant shedding phase is a normal and temporary part of recovery that most patients experience after surgery. During this period, transplanted hair shafts fall out while the follicles remain alive under the skin and prepare for new growth.
Follicles respond to surgical stress by going into a short resting stage. Subsequently, they resume their growth cycle. Although visible hair loss can be concerning, it does not affect the procedure’s final outcome. Understanding the hair transplant shedding phase helps set realistic expectations and reduces unnecessary worry as regrowth begins in the following months.
Key Takeaways
- The hair transplant shedding phase is a normal, temporary response where transplanted hair falls out while the follicles remain alive and prepare for new growth.
- Shedding usually begins within the first few weeks after surgery and stabilizes by the second month, with early regrowth often appearing around 3–4 months.
- Not all patients shed the same way, as some experience visible hair loss while others notice minimal or no shedding, both of which can still lead to healthy results.
- Shedding differs from permanent hair loss because it reflects a short resting stage in the hair growth cycle, not damage to the transplanted follicles.
What the Hair Transplant Shedding Phase Is
The shedding phase hair transplant patients experience refers to the temporary loss of transplanted hair shafts after surgery. While the visible hair falls out, the hair follicles remain intact under the skin.

This response is closely related to how follicles react to surgical stress and is commonly discussed alongside shock loss hair transplant, which may also affect the surrounding native hair.
Shedding usually affects the recipient area and does not indicate damage to the donor zone.
When the Shedding Phase Starts and Ends
Shedding after hair transplant surgery typically begins within the first few weeks after the procedure. Many patients notice transplanted hair shedding between weeks 2 and 6. This timing can vary depending on the rate of healing and individual biology.
The shedding period often stabilizes by the end of the second month. Internal follicle activity continues even when no hair is visible.
@trichogenics Hair transplant before and after 🤩 #hairloss #trichogenics #hairtransplant #hairtransplantturkey #finasteride #minoxidil #malepatternbaldness #balding #dutasteride #hairlossremedy #minoxidil
♬ original sound - Trichogenics
Early regrowth commonly becomes noticeable around three to four months, consistent with patterns seen in the hair transplant recovery timeline.
Is Shedding After Hair Transplant Normal
Shedding hair after hair transplant surgery is considered a normal side effect of the procedure. It occurs because the follicles respond to surgical trauma by pausing active growth. This response does not reflect the final result.
Not all patients experience shedding in the same way. Some notice visible hair loss, while others see minimal change. Both patterns can still lead to healthy regrowth later.
Does Everyone Shed or Can It Be Minimal
Shedding intensity differs from person to person. Factors such as skin sensitivity, blood supply, and the number of grafts placed can influence the amount of hair shedding.
Some patients experience no shedding after hair transplant surgery; this is normal. In these cases, hair may enter the resting phase without visible loss. The absence of shedding does not guarantee faster results, nor does shedding predict poor outcomes.
Why Shedding Happens After Hair Transplant Surgery
Shedding occurs because transplanted follicles experience temporary stress. During surgery, hair grafts are moved from the donor area to the recipient area, interrupting their normal growth environment. This disruption triggers a pause in hair production.
The body prioritizes healing over active growth. As a result, existing hair shafts detach while the follicles prepare for a new cycle. This response is biological, not procedural, in nature.
Hair Growth Cycle and Telogen Phase
Hair grows in cycles that include growth, transition, and rest. After transplantation, follicles often shift into telogen phases, which are resting phases of the hair growth cycle.
During this time, no visible hair grows, but internal follicle activity continues. Once follicles exit the resting phase, they re-enter the growth phase and begin producing new hair shafts. This sequence explains why patience is necessary after shedding.
What to Do During the Shedding Phase
During the shedding phase, the most important step is to adhere to postoperative instructions closely. Gentle washing, avoiding friction, and protecting the scalp support healthy recovery.
Patients should focus on consistency rather than intervention. There is no proven method to stop shedding once it begins, but proper care supports follicle survival and future growth.
Helpful actions during this phase include:
- Following the washing and care instructions provided by the clinic
- Avoiding scratching or rubbing the transplant area
- Attending scheduled follow-up appointments
Clear guidance during this time is part of structured post hair transplant care, which supports long-term graft survival.
@trichogenics You got a hair transplant… now what? Here are some recommendations for your hair transplant recovery and aftercare. #hairtransplant #hairtransplantturkey #balding #malepatternbaldness #finasteride #minoxidil #hairtransplantresult #hairloss #trichogenics #hairtransplantmexico
♬ original sound - Trichogenics
Care, Monitoring, and Medical Guidance
Medical follow-up plays an important role in surgical care. Structured monitoring allows clinicians to assess healing and address concerns early. At Trichogenics, procedures are doctor-led, which supports accurate evaluation during recovery.
Patients considering treatment abroad should be cautious. Some countries, including Turkey, operate with limited regulation and inconsistent physician involvement.
In contrast, Israel and Greece maintain stricter medical oversight, which supports safer surgical planning and follow-up.
Shedding Phase vs Permanent Hair Loss
Shedding should not be confused with progressive hair loss. Shedding is temporary and associated with surgical stress, whereas hair loss involves follicular miniaturization or damage.
Understanding this difference helps patients interpret changes correctly. Shedding affects transplanted grafts first, while hair loss may affect surrounding hairs over time if underlying conditions persist.
Transplanted Hair vs Existing Hair
Transplanted hair shedding involves hair shafts placed during surgery. Existing hair near the transplant area may also thin temporarily due to stress.
This response often resolves, as in patterns described in cases of scab formation after hair transplantation, where early-healing changes improve over time.
Donor hair follicles are genetically resistant to common hair loss patterns and usually resume growth once healed.
Does Hair Grow Back After the Shedding Phase
Yes, hair grows back after shedding in most cases. New growth starts slowly and may appear thin at first. This early hair thickens over time as follicles mature.
Growth continues gradually over several months. By the end of the first year, patients usually see a more stable and complete appearance, depending on the number of grafts and individual response.
Typical regrowth milestones include:
- Early growth signs at 3-4 months
- Increased density between months six and nine
- Ongoing refinement up to twelve months
Final Results After the Shedding Period
The final result of a hair transplant depends on surgical planning, follicle survival, and patient biology. Shedding does not reduce the long-term potential of transplanted grafts when performed correctly.
Modern techniques such as FUE and DHI, including Choi pen implantation, aim to support precise graft placement and healing.
With proper follow-up and realistic expectations, the shedding phase becomes a transitional step rather than a setback in the overall hair restoration process.
Why Choose Trichogenics?

All procedures are performed only by doctors
The uniqueness of Trichogenics lies in its strict medical process; only certified doctors perform every transplant. No technicians or unqualified assistants are involved. Choosing a clinic with proven experience in hair transplants can make all the difference.
Meet Dr. Asi and Dr. Eric Peretz
The two doctors leading Trichogenics, Dr. Asi Peretz and Dr. Eric Peretz, are recognized leaders in the field. Their extensive experience, attention to detail, and focus on natural results make Trichogenics the best choice.
Contact Trichogenics today to schedule a personal consultation and get a clear, doctor-led plan for your hair restoration.